This is the
MISO project
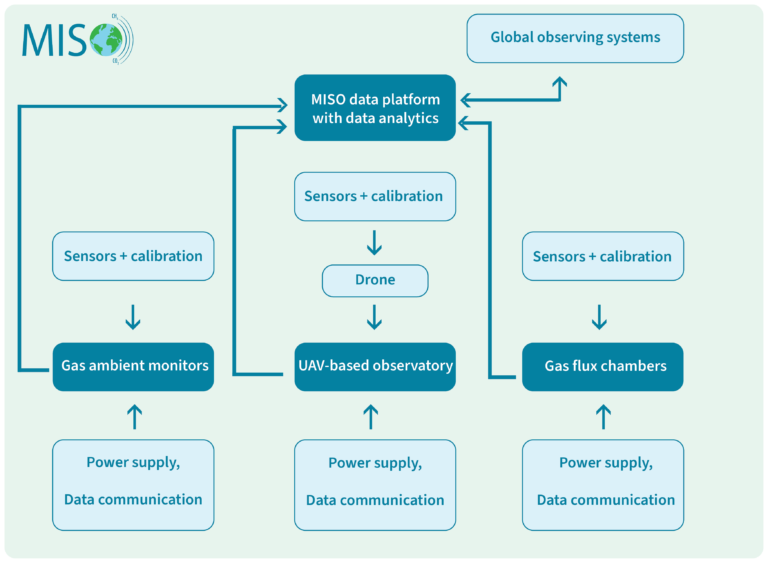
MISO develops an autonomous observation system for monitoring of emissions of CO2 and Methane, the two most important greenhouse gases. The system is modular and is suited for use in hard-to-reach areas such as the Arctic or wetlands. It combines three observing platforms (a static tower-Gas ambient monitor , a static gas flux chamber and a UAV-based observatory using NDIR sensing technologies ) with a cloud platform. The system can be operated remotely , with minimum on-site intervention.
The MISO team has expanded existing technologies: we have improved detection limit and accuracy of an NDIR GHG sensor integrated in the platforms. The static platforms and the drone base are powered by a unique geothermal device. The communication between the three observing platforms and a data cloud uses a combination of Peer2Peer, G4/G5/LTE, LORAWAN and wifi technologies.
To ensure consistent measurements, the observing platforms are optimized for energy efficient autonomous operation. This includes on-platform detection of faults through an optimized Machine Learning calibration. The cloud platform stores model updates and fault detection information together with the raw measurements.
The system is co-developed with stakeholders from academia, monitoring and measurement systems, industry and policy. It is thoroughly documented and has been demonstrated in the Arctic and in Wetland .
NEWS

🌍 MISO 2026 Consortium Meeting – Bologna
On 18–19 February, the MISO partners gathered at CNR’s headquarters in Bologna, Italy, for two productive days of technical discussions and strategic planning as we enter the final phase of the project. We aligned on progress and next steps, with strong focus on 𝐦𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐝𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐬, 𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐥𝐚𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐭𝐲, 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐚𝐫𝐝𝐢𝐳𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 of MISO

🌍 MISO Workshop Recap
Last week, we hosted the MISO workshop and were pleased to see engaging discussions and valuable exchanges throughout the session. A total of 40 participants joined to share experiences, compare strategies, and discuss the practical challenges encountered when developing and deploying new technologies to measure CO2 and CH4, especially in
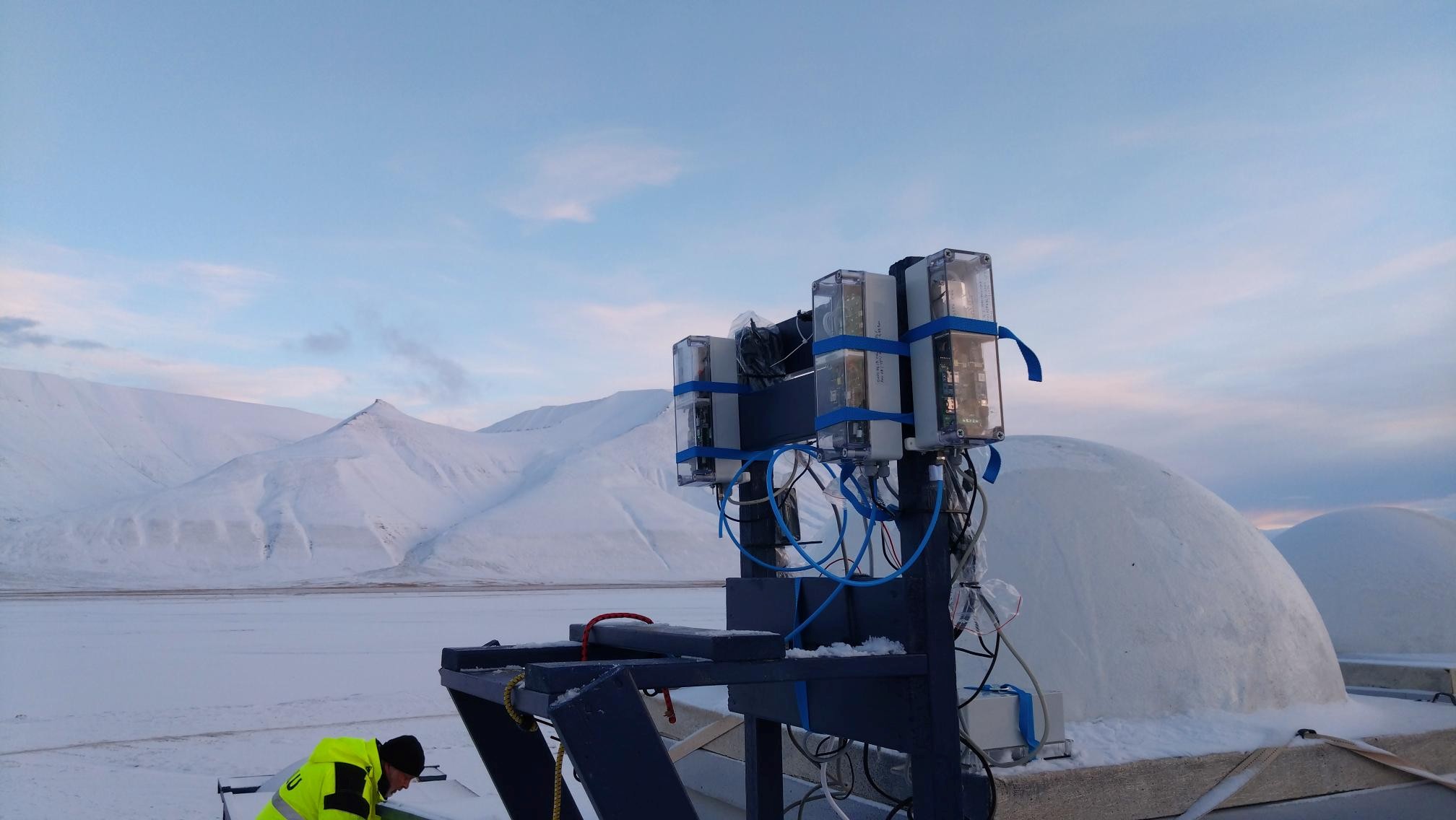

🌐❄️ MISO Svalbard – Full System Field Test
The MISO project focuses on developing innovative solutions for measuring methane and CO₂ emissions in Arctic conditions. The goal is to detect emission hotspots using drones, monitor soil emissions via flux chambers, and measure atmospheric concentrations with stationary sensors. Senseair contributes advanced sensors such as the K96, integrated into a
Contact Info
Dr. Tuan-Vu Cao, project coordinator.
The Climate and Environmental Research Institute NILU.

This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 101086541.








